In today’s world, where cloud technology is a key part of modern software solutions, SaaS (software as a service) marketing is crucial in digital commerce. It’s different from traditional marketing models, with its own set of challenges and opportunities.
Businesses are attracted to cloud-based because of its scalability, accessibility, and efficiency. This means that the way we promote these digital tools must be as modern and adaptable as the technology itself.
This playbook aims to provide you with essential insights and best practices to not only keep you afloat but also help you thrive in the bustling SaaS industry.
Understanding SaaS Marketing
Taking a deep dive into SaaS marketing, we grapple with a sector that’s complex and constantly changing, largely due to the intangible nature of its product – software as a service. Unlike physical goods, SaaS requires a different approach to selling, onboarding, and retaining customers.
SaaS marketers have to guide customers through learning about the product, getting interested in it, and finally committing to a purchase. It’s about sharing the right details at the right time to help customers make that choice, all while showing the ongoing benefits of the service in an industry where new rivals pop up quickly.
Defining SaaS Marketing
Essentially, SaaS marketing is a type of marketing that focuses on selling subscription-based software services online. It includes strategies to attract, engage, and retain customers who use digital products that constantly evolve and improve.
SaaS marketing must quickly demonstrate how useful or valuable the service is because customers can’t physically touch or see the product. This type of marketing involves clearly explaining the benefits of features that might be complex and highly technical and thus requires a marketing approach that focuses on educating customers and being transparent and deeply connected to their success.
Evolution of Saas Marketing
SaaS marketing has been shaped by technological advancements, shifts in consumer behavior, and changes in software services themselves.
In the early days, the focus was on educating the market on the benefits of the SaaS model, such as scalability and cost-effectiveness. Today, there’s greater emphasis on building long-term relationships with customers through personalized marketing, data-driven decision-making, and a focus on customer experience.
Moreover, SaaS marketing now uses more channels, from content marketing and SEO to account-based marketing and influencer partnerships. Experts are leveraging AI and machine learning for predictive analytics and advanced customer segmentation. It is all in a bid strategy to deliver the right message to the right user at the right time.
The future of SaaS marketing depends on its ability to be flexible and innovative. Businesses must account for emerging trends, such as the need for data privacy, the demand for on-demand services, and the impact of new technologies on traditional SaaS sales processes. It’s a dynamic field, and for SaaS companies, staying ahead in their marketing is essential.
Understanding SaaS marketing is like mastering how to connect with modern consumers in an environment that’s constantly in flux. As we move into 2024 and beyond, the key for SaaS businesses will be to continuously adapt, innovate, and stay attuned to the needs and behaviors of their customers.
Distinctive Features of SaaS Marketing
SaaS marketing differs from traditional marketing strategies in its approach, execution, and measurement. Its distinct characteristics aren’t just about selling a product; they’re about fostering a continuous relationship with the customer and providing a service that evolves over time.
Product-centric Marketing
Marketing a SaaS product requires understanding the software’s features and the problems it solves.
Unlike physical goods, SaaS products demand experts to demonstrate their value through live demos, free trials, and detailed product walkthroughs. Marketers must explain what the product does and how it fits seamlessly into the customer’s workflow or business operations.
The Importance of the Customer Journey
SaaS marketing is closely tied to the customer’s experience, which is more complex and has multiple stages because the service is based on subscriptions.
Awareness
The awareness stage in SaaS marketing is about making prospective customers see your product as a solution to a problem. This is done by providing educational content strategy, showing expertise, and having a strategic online presence.
Consideration
In the consideration phase, potential customers are weighing their options. SaaS specialists must help them decide with messages that meet their exact needs, success stories, and reviews from other customers.
Decision
The decision stage is critical in turning prospects into active users. To convince them, marketers should use persuasive messages, offer free trials, and give convincing demos to show the immediate benefits of adopting the SaaS solution.
Adoption
When a number of users start using the product, their experience is most important. Specialists need to ensure that new customers find value quickly by providing a good introduction to the product and responsive customer support.
Retention
Retention is crucial in SaaS marketing because the business keeps earning from them. Marketers work to keep users interested and happy for a long time by regularly updating them, reaching out to them personally, and creating a sense of community among users.
Advocacy
Advocacy is the final step in the user journey, where happy customers start promoting the brand themselves. At this stage, positive customer experiences are used to encourage more recommendations, using the power of word-of-mouth and social proof.
Pricing Models in Saas Marketing
Unique pricing strategies in SaaS marketing are key for gaining and keeping customers, so how a product is priced is a big part of the marketing message.
Freemium Pricing
The freemium model operates on the premise of offering a basic version of the software for free while reserving more advanced features for paid plans. This strategy for SaaS works as a powerful lead magnet that draws users to experience the product with the aim of converting them to paying customers over time.
The challenge is to offer enough in the free version to hook users but save some key features for the paid version to encourage users to upgrade.
Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing structures are designed to cater to a wide range of users, from small businesses to large enterprises. Each tier offers a progressively richer set of features and benefits, encouraging customers to scale their subscriptions as their needs grow.
For marketing experts, the tiered approach allows for targeted messaging and segmentation, aligning marketing initiatives more closely with the various customer profiles.
Usage-Based Pricing
The usage-based model, or pay-as-you-go, resonates with customers who prefer costs to match their use. This model is appealing because it offers transparency and flexibility, allowing users to control their spending based on how much they use the service. For SaaS companies, this can mean earnings that grow with the customer and the service.
Per-User Pricing
Per-user pricing is a straightforward model where the cost increases with each new user of the software. It’s easy to understand and fair for customers since they pay according to their team size. However, SaaS companies need to balance the price per user so that it’s fair for both the business and its customers.
Flat-Rate Pricing
A flat-rate model offers full access to a SaaS product for one fixed price. It’s straightforward, making it attractive for customers looking for an all-inclusive solution without the worry of other costs. This clarity helps marketing experts by making it easier to communicate and speeds up the sales cycle.
Contract-Based Pricing
Contract-based pricing means a customer agrees to use the service for a set period, often in exchange for discounted rates. This model can benefit both parties by providing customers with cost savings over time and granting SaaS providers a steady income. Marketers can use these contracts to build long-term relationships and reduce customer churn.
Bundled Pricing
Bundling involves offering a set of products or services together at a lower cost than if purchased separately. It’s an excellent strategy for highlighting the variety of a SaaS platform and encouraging the use of other features or services. While it can simplify the buying process, marketing specialists should clearly communicate the benefits of the bundle versus a la carte options.
Implement a Tactical SaaS Marketing Plan
A tactical SaaS marketing plan is your guide that outlines the specific steps to get new customers, keep them, and grow your business. Each step should be precise and deliberate, aiming toward your set marketing goals.
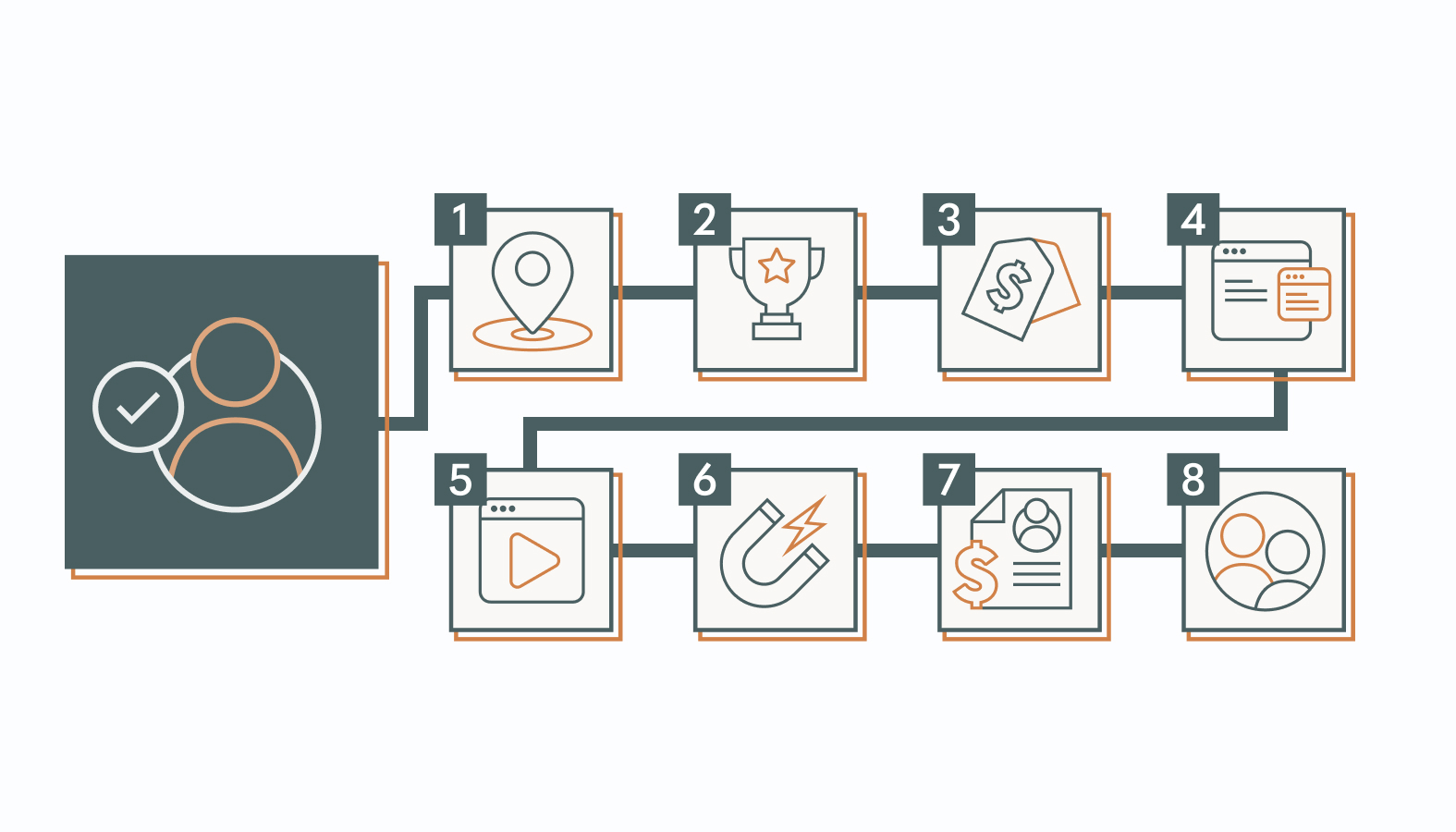
Step 1: Identify Your Target Audience and Buyer Personas
To effectively market your SaaS product, you need to understand who will benefit most from it. Conduct detailed market research to identify your target audience’s demographics, behaviors, and preferences. From this data, create customer personas of your ideal customers, including their job, industry, company size, and problems. This is crucial for personalized marketing strategies.
Step 2: Develop a Value Proposition
Your value proposition explains why customers should choose your SaaS offering over competitors. It should be clear, concise, and compelling. Focus on the unique features of your product and how it makes a difference in your customers’ lives or businesses.
A strong value proposition resonates with your identified buyer personas, emphasizing how your product solves their specific problems or improves their situation.
Step 3: Establish a Pricing Model
Choose a pricing model that matches what customers think your SaaS product is worth and what they can afford. Your chosen model should show the value of your product, fit with the market competition, and support your long-term business goals. Consider how much the demand for your product might change with different prices and find a strategy that maximizes profitability without turning away potential customers.
Step 4: Build a Conversion-Focused Website
Your website is often the first point of interaction between your product and a potential customer. As such, it should be designed to convert visitors into customers. A conversion-focused website has an intuitive layout, a smooth user experience, clear and persuasive copy, and strong calls to action. It should explain the benefits quickly, provide easy access to product information, and guide visitors toward the next steps, such as signing up for a free trial or requesting a demo.
Step 5: Create High-Quality Content
Content marketing can attract and engage potential customers by offering value through informative and engaging marketing material. Develop a content marketing strategy that addresses your target audience’s pain points and positions your company as a knowledgeable authority in your space.
Use a mix of blog posts, whitepapers, videos, webinars, and infographics to cater to different preferences and stages of the buyer’s journey.
Step 6: Increase Web Traffic and Lead Generation
In promoting and generating leads for customers, you need a steady flow of traffic to your site. Use SaaS SEO to increase organic search visibility, engage in pay-per-click campaigns to target specific keywords, and maintain an active presence on social media platforms where your potential customers spend their time.
Each marketing channel should be carefully monitored and optimized for lead generation to ensure your marketing initiatives bring a good return on investment.
Step 7: Convert Visitors to Customers
Converting visitors into customers is the goal of your marketing efforts and should be done with precision. Effective strategies include using persuasive landing pages, offering live product demonstrations, providing testimonials and customer success stories, and ensuring a smooth sign-up or purchase process. Focus on building trust and removing any barriers to conversion.
Step 8: Focus on Customer Retention
In the SaaS industry, retaining customers is as important as acquiring new ones. Implement customer retention strategies like offering exceptional customer support, sending regular product updates, gathering and acting on customer feedback, and creating a community around your product. Satisfied customers tend to stick around and recommend the brand to others.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
In the competitive world of SaaS marketing, theory only carries you so far; the real test comes with execution. To show how effective new SaaS marketing works, let’s explore some real-world examples. These case studies are more than just an inspiration; they show us what’s possible with a good strategy.
Case Study Breakdowns
Let’s look at how some of the big names in the industry have used effective SaaS marketing strategies successfully and see what we can learn from their tactics.
Salesforce
This CRM giant is known for its customer-centric approach. What sets it apart is its ability to create a seamless customer journey, from acquisition through to advocacy.
It uses consistent messaging, educational webinars, and extensive knowledge sharing, making it a key part of its users’ work. It always aims to provide ongoing value, as seen in its updates and how it interacts with its community. This approach has earned them loyal customers who actively promote the brand.
Slack
The rise of Slack from a simple messaging tool to an integral business communication platform is a masterclass in SaaS marketing. Its initial strategy used word-of-mouth, fueled by a strong product that people enjoyed using.
Slack’s focus on a clean, intuitive user interface and its integration capabilities with other tools made adoption a breeze. Its marketing efforts focused on this ease of use, with fun and relatable SaaS marketing campaigns that appealed to a tech-savvy audience looking for efficient work solutions.
A great example of its strategy is sharing users’ compliments on the “Slack Wall of Love” on Twitter, which shows how happy customers helped promote the app.
HubSpot
A pioneer in inbound marketing. HubSpot’s marketing approach is a study in the art of drawing customers in rather than reaching out. By offering a wealth of valuable content, such as blogs, e-books, and courses, it has managed to turn its website into a knowledge hub that attracts visitors naturally through search engines and social shares.
It also provides free tools that solve immediate needs, which makes every potential customer familiar with HubSpot before they consider buying. This freemium model, along with their thorough content marketing efforts, has successfully converted many users into leads and, ultimately, paying customers.
Learning From Market Leaders
The success stories of these top SaaS companies offer valuable lessons.
Salesforce shows us that a marketing plan that changes with customer needs can be very powerful. Slack’s rise proves that if a product is good enough, people will naturally want to use and share it. HubSpot’s success teaches us that giving customers the knowledge and tools they want builds trust and sets a company up as an expert.
For SaaS companies wanting to use these marketing techniques, the key is to adapt, not just adopt. You need to understand the core principles that made these strategies successful – customer-centricity, seamless user experience, and educational value –and then apply them in a way that aligns with your brand and audience.
The goal is to stay flexible, keep the customer in mind, and be ready to adjust when needed. By staying in tune with the industry and continually refining marketing approaches based on real-world feedback and data, you can succeed in the ever-changing digital market.
How to Measure SaaS Marketing Success
Every SaaS marketer knows that without the numbers to back it up, “success” is just another word in the dictionary. In SaaS marketing, it’s critical to accurately measure success. Whether you’re a bootstrapped startup or a scaling enterprise, the ability to measure the effectiveness of your marketing efforts is non-negotiable.
Luckily, there’s a suite of metrics designed to do just that so you know whether your marketing strategies are hitting the mark or missing the target. Let’s explore them one by one.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC is a key measure that shows how much you’re spending to get new customers. It’s calculated by adding up all your marketing and sales costs for a certain period and dividing that by the number of customers you gained in that time.
Knowing your CAC is like checking how healthy your business is – it tells you if you’re spending too much or just the right amount to attract customers.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
If CAC tells you how much you’re spending to acquire customers, CLV tells you their worth over time. CLV is a forward-looking metric that projects the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. It considers how much customers spend, how long they stay subscribed, and whether they upgrade to more expensive services.
CLV is vital because it helps you decide how much money you should spend to get new customers and keep existing ones and how to make your business more profitable over time.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
MRR and ARR are crucial numbers for a SaaS business. They show the steady income from subscriptions you can expect monthly and yearly. Keeping an eye on MRR and ARR helps you plan for the future, decide where to spend money, and see how well your strategies for getting and keeping customers are working.
Conversion Rate
Conversion rate is a measure that shows how well your website turns visitors into customers or leads. It’s found by comparing the number of people who do something you want (like signing up or buying) against the total number of visitors. The goal of SaaS marketing is to improve this rate. It is making sure you get as many new users as possible from the people visiting your site.
Churn Rate
Churn rate measures how many customers stop using your service over a certain period. It’s the opposite of growth – if your churn rate is high, it means you’re losing customers, which can lower your income and the total profit you expect from each customer. Nonetheless, a high churn rate can also signal problems with your product or that customers aren’t happy.
Website Traffic
Website traffic is about how many people visit your website and how interested they are in what you offer. It’s important to attract visitors, but it’s also key to understand where they come from and what they do on your site.
Looking at where visitors are coming from, how long they stay, and how many pages they look at helps you know what they like and if your content and SEO are working well.
Brand Search Volume
Brand search volume is how often people search for your brand or products by name on the internet. It shows how well-known your brand is and suggests that your marketing efforts may be working if many people are looking you up. A lot of brand searches can mean that your company is getting popular and that people are talking about it.
Future-Proofing Your SaaS Marketing Efforts
In an industry that moves as quickly as SaaS, staying ahead isn’t just about keeping pace. Your marketing strategies need to be as flexible and forward-thinking as the services you’re offering. It’s about being ready for tomorrow, today.
Embracing New Technologies
Keeping your SaaS marketing fresh and effective means staying open to new technologies. Artificial intelligence, for example, is becoming a staple, automating tasks and personalizing customer interactions. Big data gives you a clearer picture of what your customers want, and blockchain promises safer, more transparent transactions.
Innovations like augmented and virtual reality are also on the rise, offering immersive ways to showcase your software. By integrating these technologies into your marketing approach, you’re not just staying current – you’re pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Maintaining Scalability and Adaptability
Your marketing should grow with your business, smoothly handling more customers without dropping the ball. But being scalable isn’t enough; you must also be adaptable and ready to adjust your tactics in response to new data, customer needs, and what your competitors are doing.
This balance means you can pursue new opportunities and make changes without slowing down or compromising quality.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
In SaaS marketing, the learning never stops. The most successful marketing teams embrace this, always hunting for the latest knowledge. That means reading up on trends, joining webinars, networking with peers, and taking courses to sharpen your skills.
Staying educated not only keeps your marketing game strong but also sparks innovation and creativity. When you’re always learning, you’re building a marketing strategy that doesn’t just cope with the future but shapes it.
SaaS Marketing: Bringing It All Together
SaaS marketing is a dynamic field that demands innovation, insight, and adaptability. The key to success here is making your marketing SaaS product stand out, understanding your customer’s journey, and being quick to adapt to new changes in the industry.
If you’re seeking to deepen your understanding of SaaS marketing and explore its potential to grow your business, our experts are here to help. Schedule a candid conversation with us to learn how these strategies can be tailored to your unique context and goals.